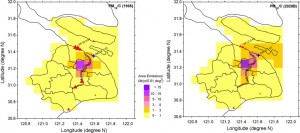

Shanghai: PM10 and PM2.5: These particles are caused by dust or emissions from vehicles, factories, construction sites and coal combustion. Fine particulates (PM2.5) can penetrate lungs and enter the bloodstream, making them the most detrimental to health. As you’d expect, chronic exposure leads to an increased risk of health issues, particularly heart disease and lung cancer. Sulfur dioxide, NH3, and nitrogen dioxide are a large amount of what makes up the mass of pollution. Normal working hours when the factories are operating tend to be the worst for air quality, and even more so in the commuting hours before and after. This is generally from 7AM-6PM.
Factors Already Employed to Prevent Pollution:
- PM2.5 monitoring stations are to be introduced to 30 cities nationwide (including Shanghai).
- Shanghai is by the sea, which helps to rapidly clear the air.
- Five-Year Plan on Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Introducing Accountability System for Performance Assessment: The Plan also calls for redoubled effort of denitration and desulphurization in electric power industry and non-electric power industries. Flue gas desulphurization will be applied to sintering machines and the desulphurization rate of all sintering machines and pellet production equipment in built area of cities. Electric power, iron & steel, papermaking and printing & dying industries will be subject to total pollution control while newly built and extended projects will be managed by replacement of pollution discharge with equivalent or reduced amount.
- Some wear surgical masks.
- Avoiding being outdoors in the main metropolitan area.
Tokyo:
Causes:
- Smoke factories
- Vehicles and fumes emitted by diesel-powered vehicles (main cause)
- Burning a agricultural products. Ex: hay.
- Tobacco smoke
- Exhaust gas from fossil fuels that is used for thermal power generation also includes nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides and causes the air pollution
Particles:
CO, NO2, SO2, TSP, HC
Prevention:
- Tokyo Metropolitan Government (TMG) started to restrict diesel-powered vehicles in collaboration with the eight local governments in the Kanto district.
- Fixed emission sources, such as strict control of air pollutant sources, including boilers, and use of higher quality fuel
- Promotion of public transportation and bicycle usage.
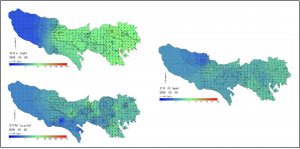
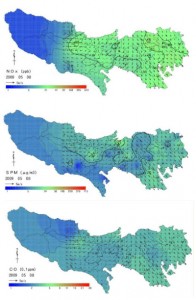
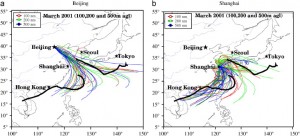
The east side of Tokyo in the map is where 23 wards are located while west side is where the rest of cities are. As you can see, the levels of air pollution are relative low in the west side of Tokyo in all cases. The east is where most industrial production occurs, which influences the larger amount of vehicular travel. Winters and summers are said to the worst. In the winter the northern winds blow pollution from Shanghai and Beijing over to Tokyo.
Beijing:
Causes:
- Hazardous heavy metals found in the air over Beijing come from ferrous metal smelting and coal burning in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area.
- Vehicles and fumes emitted by diesel-powered vehicles (main cause)
- Tobacco smoke
Particles:
CO, NO2, SO2, TSP, HC
Prevention:
- The government regularly uses cloud-seeding measures to increase the likelihood of rain showers in the region to clear the air prior to large events.
- Beijing has added 3,800 natural gas buses, one of the largest fleets in the world.
- The city has also planted hundreds of thousands of trees and increased green space in an effort to make the city more livable.
- Daily pollution readings at 27 monitoring stations around the city are reported on the website of the Beijing Environmental Protection Bureau (BJEPB). This allows the public to know when being outdoors is safer in a sense.
- Most of the population wears surgical masks when outdoors.
- Halted construction during Olympics, only allowed those there for the games into the city, and promoted the lowering of vehicular use during the time.
Vehicle emissions are largest in Beijing’s downtown area. Summers are said to be the worst. Prevailing south/southeasterly flow during the summer and the mountains to the north and northwest are one of the infuencing factors. During the Beijing Olympics, emissions were at their lowest in the past decade. They wanted the quality to be the best it could for the atheletes.